IMPACT
 1
1What is aging?
Aging is a universal process that affects all species on the planet, including humans. This process is characterized by a gradual decline in our abilities and functional capacity of organs. The human body reaches its peak performance during the first three decades of life. Hearing is at its peak around the fifth year of life, we reach our maximum strength at around the age of twenty, and the immune system functions most efficiently during the period after compulsory schooling.
How does aging occur?
Aging starts at the molecular and cellular level. During every metabolic process in the human body, small errors occur that are not significant in themselves. However, these errors accumulate over time and lead to the manifestations known as aging. We can classify these errors into basic categories, which we refer to as 'signs of aging'.
 2
2
BASIC SIGNS OF AGING
Initially, research suggested that there were just nine basic signs of aging. But now we know that the number of signs of aging can be as many as twelve...
The original signs include genomic instability, telomere shortening, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Recent scientific evidence suggests that hidden chronic inflammation, impaired autophagy or microbial imbalance may be equally important signs of aging.
The Minus Age project targets and effectively prevents these signs.
 3
3Hidden chronic inflammation
Hidden chronic inflammation, also called "inflammaging", is one of the key signs of aging. This type of inflammation is characterized by its longevity and low-level manifestation. It is caused by the accumulation of damage at the molecular level and dysregulation of the immune system.
Chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of many diseases. With age, the risk of cardiovascular disease, the incidence of diabetes or neurodegenerative disorders increases. Research shows that targeted prevention aimed at reducing chronic inflammation can significantly reduce the incidence of these diseases and improve quality of life even in advanced age.
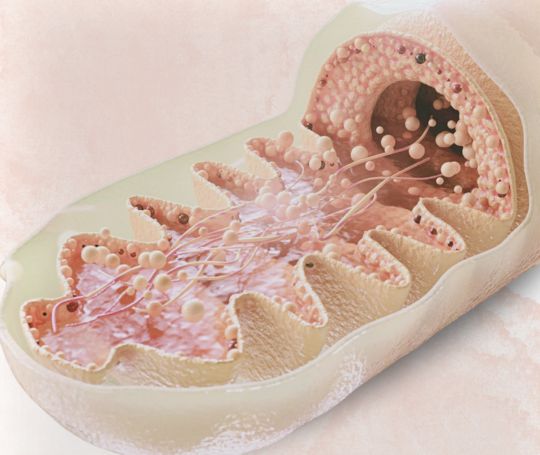
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Our body's cells use mitochondria, sometimes called "cell factories", to create energy. Due to the accumulation of errors at the cellular level, their function declines over the course of life. The human body is thus unable to process the energy obtained from food efficiently. One compound that can help cells is a substance called NAD. It is naturally found in cells and plays a key role in our energy production.
 4
4
How can we prevent aging?
Regular exercise and a balanced diet are the keys to optimal health and slowing aging. Physical activity not only maintains ideal weight, but also improves cardiovascular health, strengthening our muscles and bones. Regular exercise reduces stress and improves our cognitive function.
Equally important is a diet rich in antioxidants, which protect cells from damage. This can prevent chronic diseases and slow down aging. A balanced diet should include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats and protein. Limiting sugars and unhealthy fats is essential for preventing obesity, diabetes and heart disease.
The combination of regular exercise and a healthy diet is an effective way to prevent aging and helps maintain youthful energy. In addition to the basic principles, our health can be enhanced by taking appropriate dietary supplements.
 5
5NMN and NAD levels
Taking NMN helps increase NAD levels, which may slow aging and promote health. Furthermore, we already know that NMN is converted into NAD in the body, which is crucial for cellular energy and metabolic processes. Taking NMN regularly increases our energy, improves metabolic function and promotes overall vitality. Studies show that NMN also improves cognitive function and reduces the risk of chronic disease.
Today, technology allows us to effectively measure NAD levels in the body using a laboratory test.
For increased NAD and energy levels, try Minus Age NMN.
Other effective ways
Among the world's best-known antioxidants are foods rich in the substance resveratrol, which is abundant in grapes. Minus Age Resveratrol may help slow aging through its antioxidant effects and regulation of blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
With increasing age, there is a loss of muscle mass. Minus Age Urolithin A promotes muscle strength, mitochondrial health and thus prevents premature aging.
Many studies suggest that the microbiome plays a critical role in the rate at which we age. Probiotics help us digest and absorb nutrients efficiently. They are key in protecting against civilization diseases. Minus Age Fullbiotic contains probiotics, but also prebiotics. These ingredients promote the growth of appropriate cultures that contribute to a healthy microbiome throughout the body.
And much more about our products at our: E-SHOP
 6
6
For a complete selection, visit our E-shop page.
